Oct 4, 2023
The success of every IoT deployment in the constantly changing Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem depends on provisioning, an essential but often overlooked phase. IoT provisioning is the procedure of setting up and configuring IoT devices in order to make sure they operate without a hitch within a network or ecosystem.
Understanding IoT Provisioning
When you register a new device or sensor into the system, you set it to deliver data to the system as well as authenticate it onto the organisation’s network, such as your ERP system. This provisioning includes installing device certificates and tokens on the sensors, delivering sensor data from the equipment to your system, and then upgrading your ERP to show the sensor on its appropriate piece of equipment.
Authentication is a crucial component of provisioning. Only devices with the proper certificates and credentials are verified as part of authentication. These credentials are aware of the server’s URL and are able to connect to it in order to enrol.
The device or sensor must then be configured so that it may convey the data it is monitoring through the servers or other platforms to which it is attached.
STEP-BY-STEP PROCEDURE
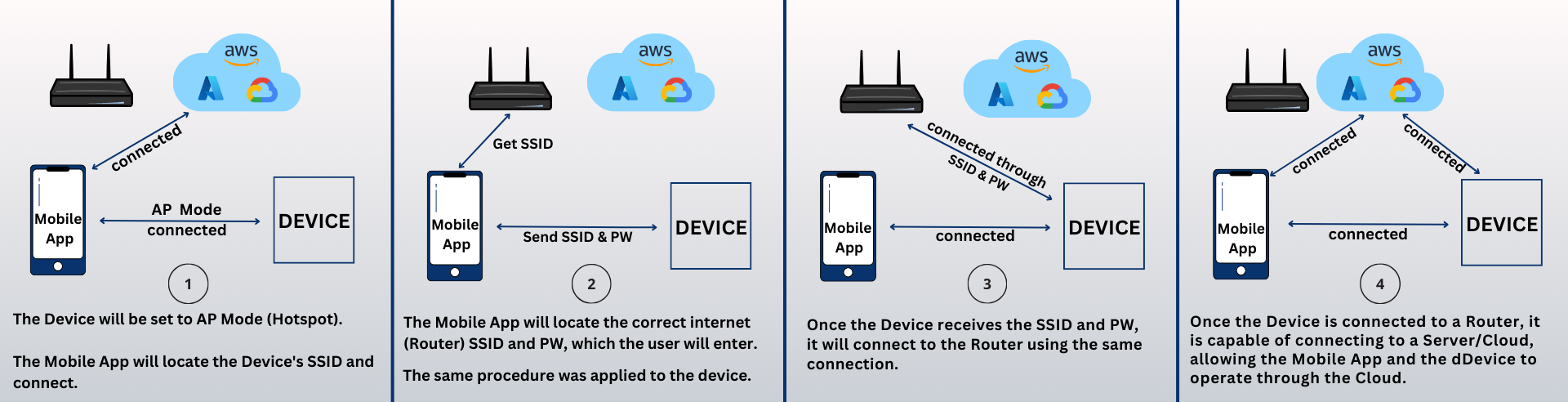
1) The Device will be set to AP Mode (Hotspot). The Mobile App will locate the Device’s SSID and connect.
2) The Mobile App will locate the correct internet (Router) SSID and PW, which the user will enter.The same procedure was applied to the device.
3) Once the Device receives the SSID and PW, it will connect to the Router using the same connection.
4) Once the Device is connected to a Router, it is capable of connecting to a Server/Cloud, allowing the Mobile App and the dDevice to operate through the Cloud.
How IoT Provisioning Works
The goal of IoT provisioning is to ensure that each device is properly set up, authenticated, and ready to function as intended. Here are some key aspects of IoT provisioning:
1. Device Initialisation
During provisioning, IoT devices are initialised, which involves tasks like setting up the device’s hardware, initialising its software, and configuring essential parameters. This can include network settings, security credentials, and device-specific configurations.
2. Authentication and Identity Management
Provisioning typically involves establishing secure identities for IoT devices. This is crucial for ensuring that only authorised devices can join the network and that communication remains secure. Common authentication methods include certificates, keys, and credentials.
3. Network Configuration
Devices need to be configured to connect to the appropriate network, whether it’s a local Wi-Fi network, cellular network, or any other type of connectivity. This includes specifying network SSIDs, passwords, and other relevant settings.
4. Security Measures
Security is a paramount concern in IoT provisioning. Devices should be provisioned with the necessary security measures, such as encryption keys, to protect data and communications. Regular updates and patches should also be part of the provisioning process to address potential vulnerabilities.
5. Remote Provisioning
In some cases, devices may need to be provisioned remotely, especially if they are in remote locations or are difficult to physically access. Remote provisioning methods enable devices to be set up and configured over the air (OTA).
6. Scalability
IoT provisioning processes should be scalable to accommodate a large number of devices efficiently. This is crucial in scenarios where thousands or even millions of devices need to be provisioned simultaneously.
7. Lifecycle Management
Provisioning is not a one-time event. IoT devices may need to be reprovisioned or updated throughout their lifecycle, whether it’s for security reasons, changing network environments, or software updates. Lifecycle management includes decommissioning devices when they are no longer in use.
8. Zero-Touch Provisioning
Zero-touch provisioning is a provisioning method that automates much of the setup process, allowing devices to join a network and configure themselves with minimal manual intervention. This is particularly useful for large-scale IoT deployments.
9. Integration with Device Management Platforms
IoT provisioning often involves integration with device management platforms or IoT platforms. These platforms help streamline provisioning processes and provide ongoing management and monitoring capabilities.
Use Cases of IoT Provisioning
Smart Home Devices: In a smart home, IoT provisioning enables the setup of smart thermostats, lights, security cameras, and other connected devices. Users can configure these devices via mobile apps or voice assistants, making them part of the home automation system.
Fleet Management: In fleet management, vehicles can be equipped with IoT devices that provide real-time location tracking, diagnostics, and communication capabilities. IoT provisioning ensures these devices are connected to the network and integrated into the fleet management platform.
Industrial IoT (IIoT): In industrial settings, IoT provisioning is critical for connecting sensors, actuators, and machines. It enables real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and process optimization.
Healthcare: IoT provisioning is utilised in Healthcare for medical devices such as patient monitors and infusion pumps. To ensure accurate data gathering and patient safety, these devices must be securely provided.
In Essence
IoT provisioning is a critical component of IoT device management because it ensures that devices are ready to perform their intended functions in a secure and dependable manner. Proper provisioning reduces deployment time, reduces the danger of security breaches, and ensures the seamless operation of IoT devices.
Provisioning for IoT devices is a key component of any IoT project, choosing the right one for the project should be your top concern.
At Ealphabits, the possibilities are limitless.
We secure the success of your product. To power your ideas, contact us at sales@ealphabits.com | +91 973720 8790 or visit our website at www.ealphabits.com.

Need help with your
Hi, I'm Hardik Kamothi,
Founder and Technology Evangelist.
I'd like to hear about you, your business, your project requirements, and assist you on how I can deliver result-oriented solutions that bring value to your business.

